Further information
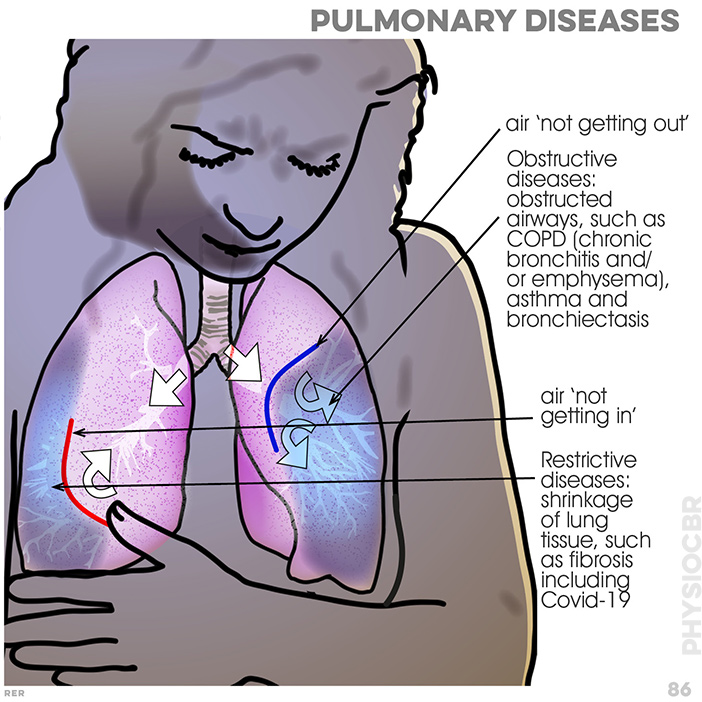
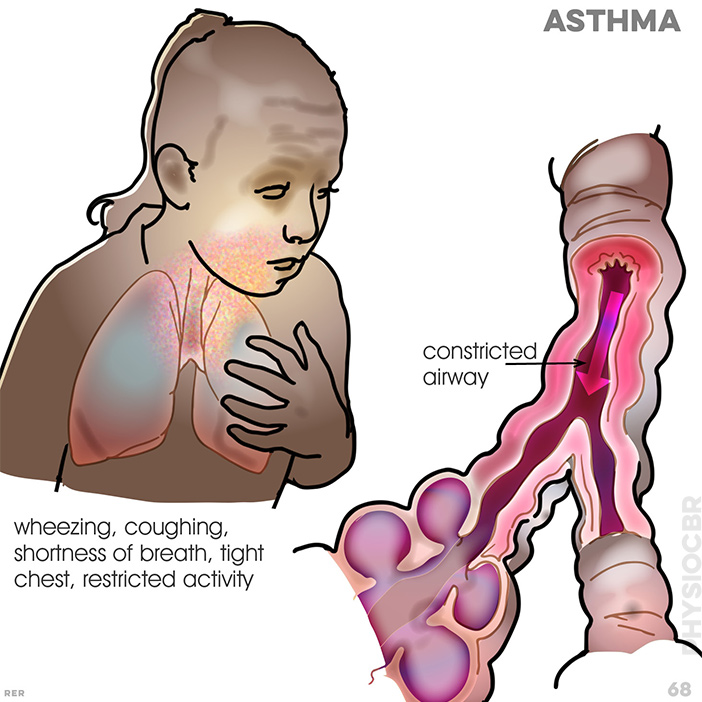
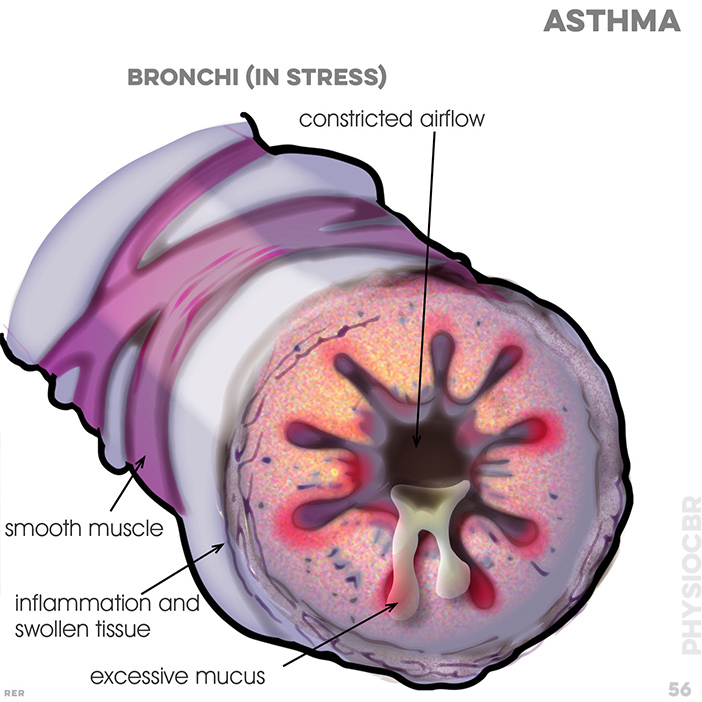
56. Asthma: bronchi are stressed with constricted airflow; smooth muscle tightens the bronchi causing inflammation and swollen tissue, with excessive mucus
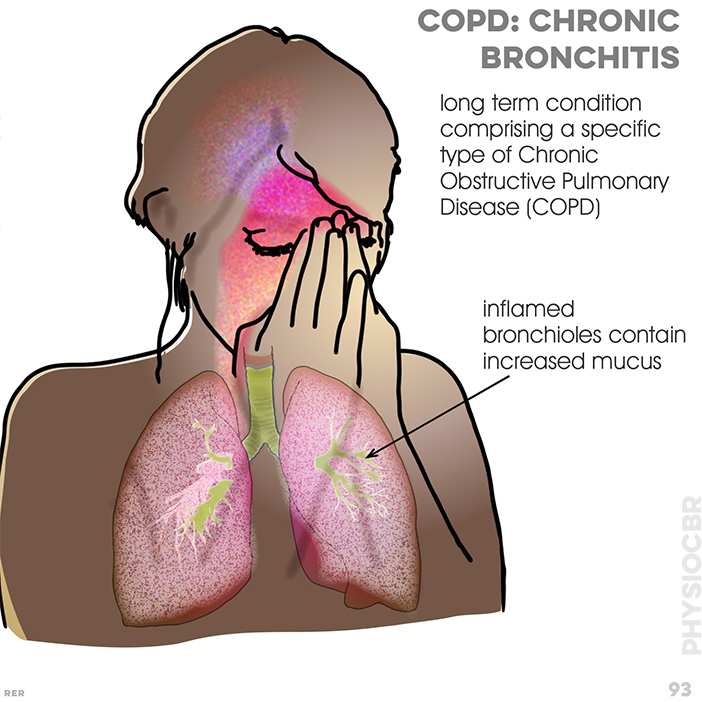
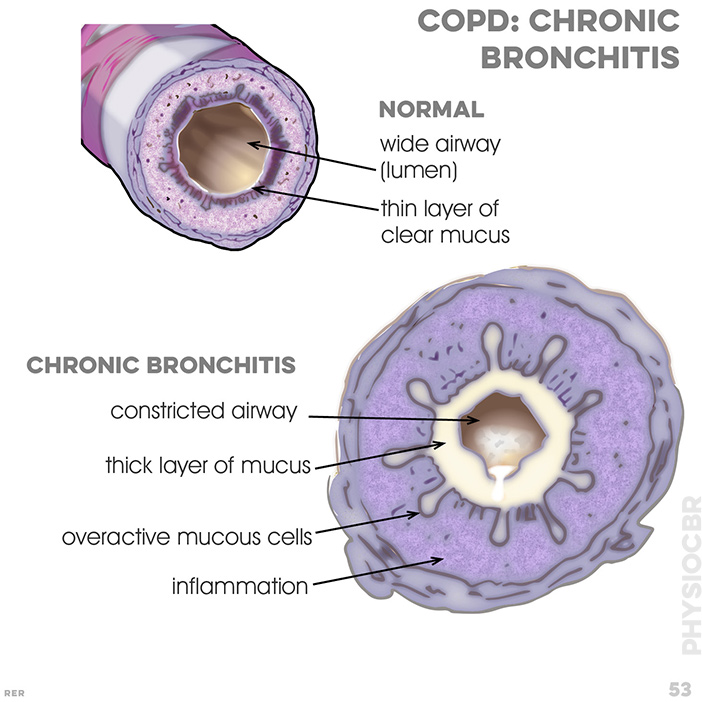
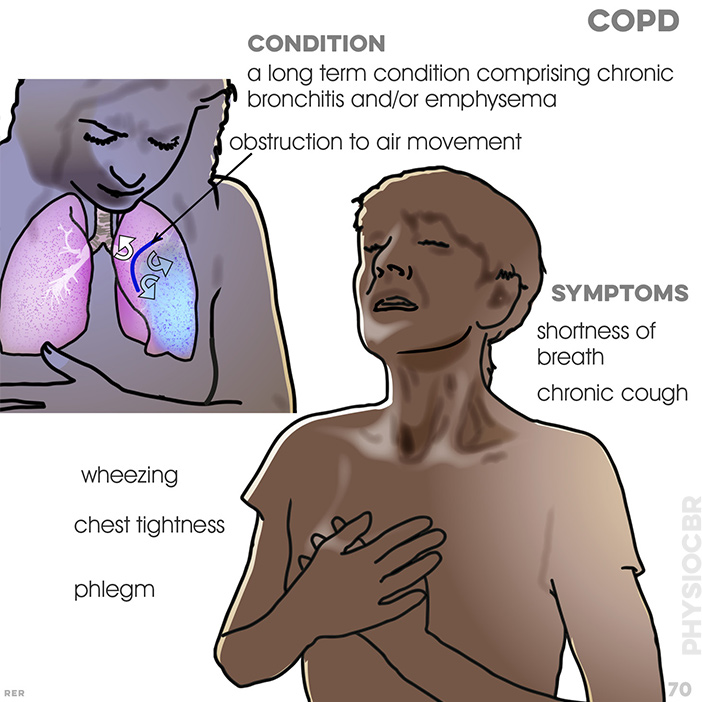
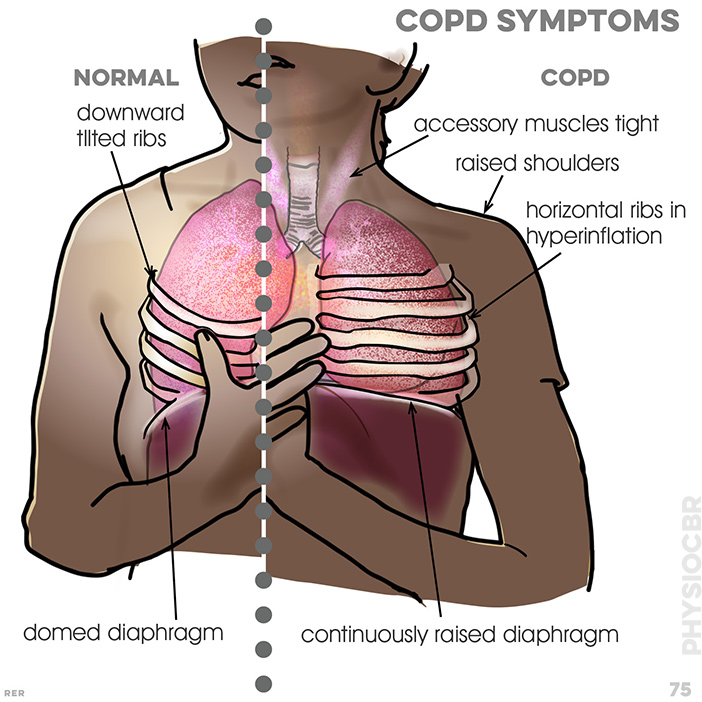
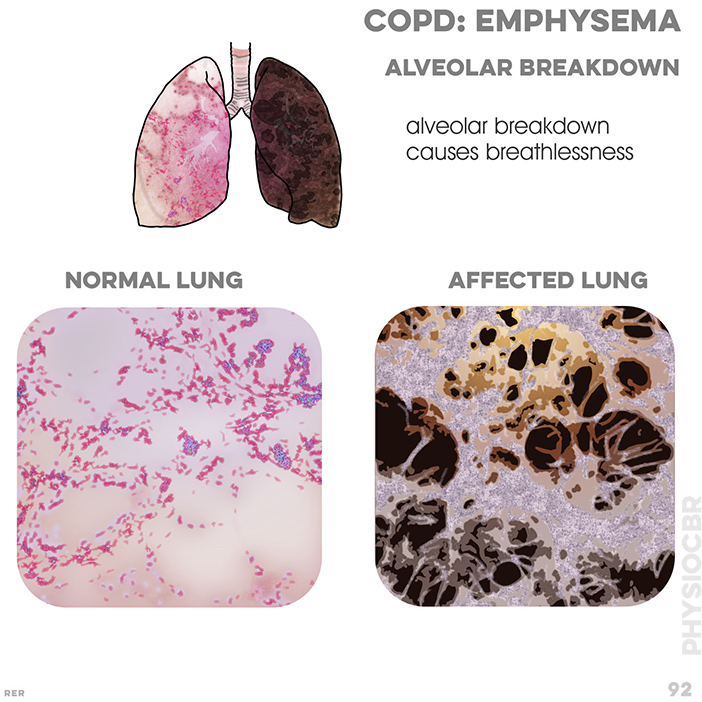
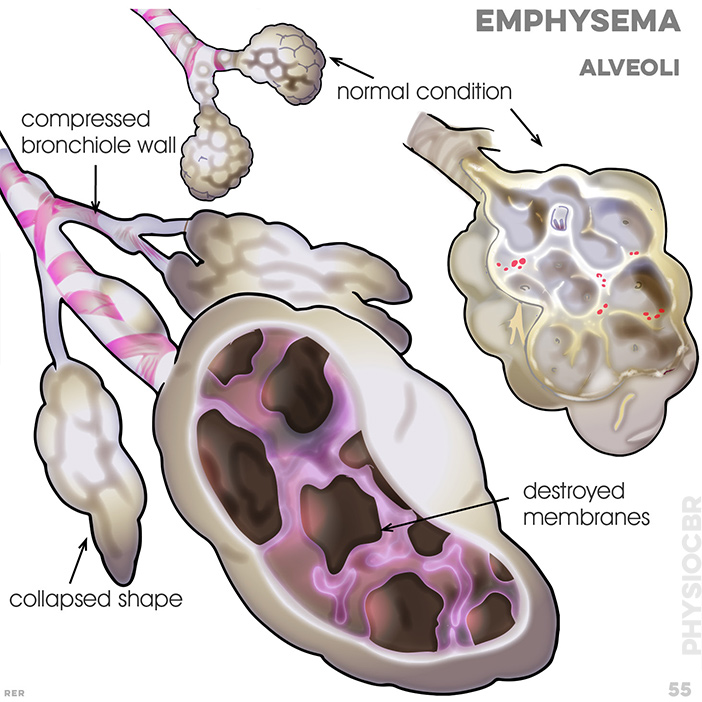
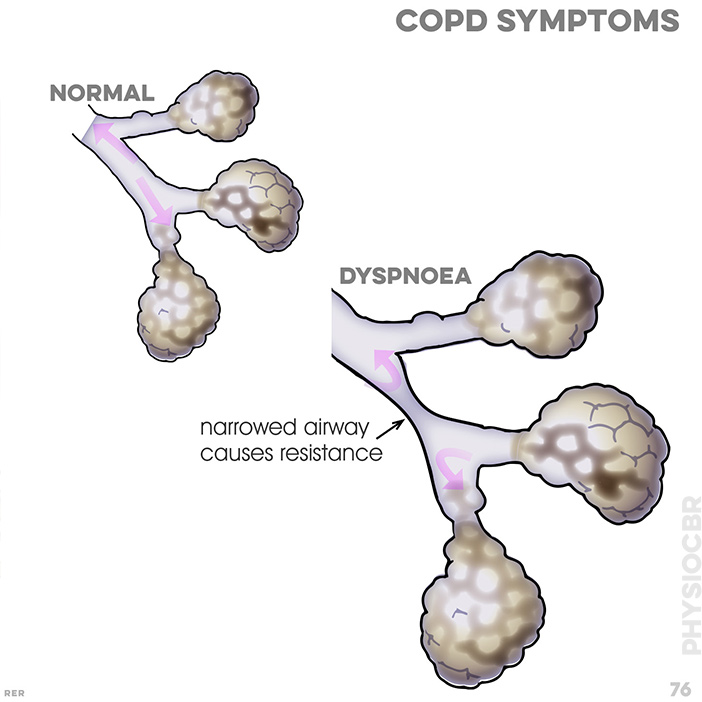
76. COPD symptoms: dyspnoea with narrowed airway, causing resistance; continued dilation causes alveoli to collapse
83. Stridor: has an abnormal, high-pitched sound that is caused by an obstructed airway making breathing difficult; (epiglottis; subglottis; vocal chords behind cartilage; trachea, oesophagus)
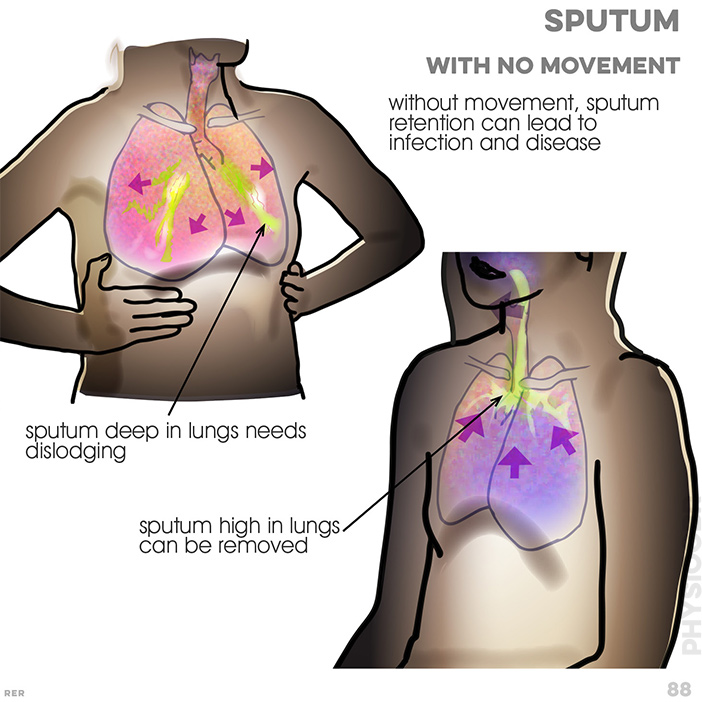
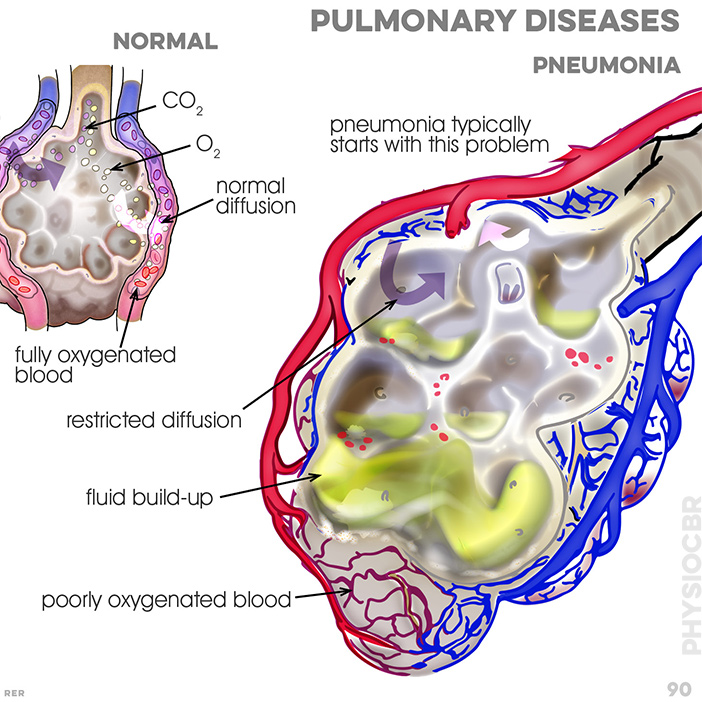
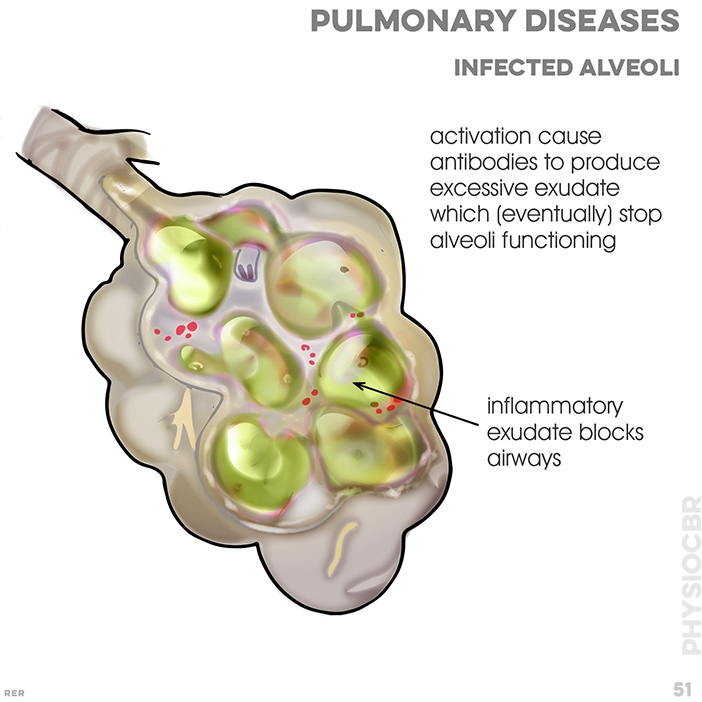
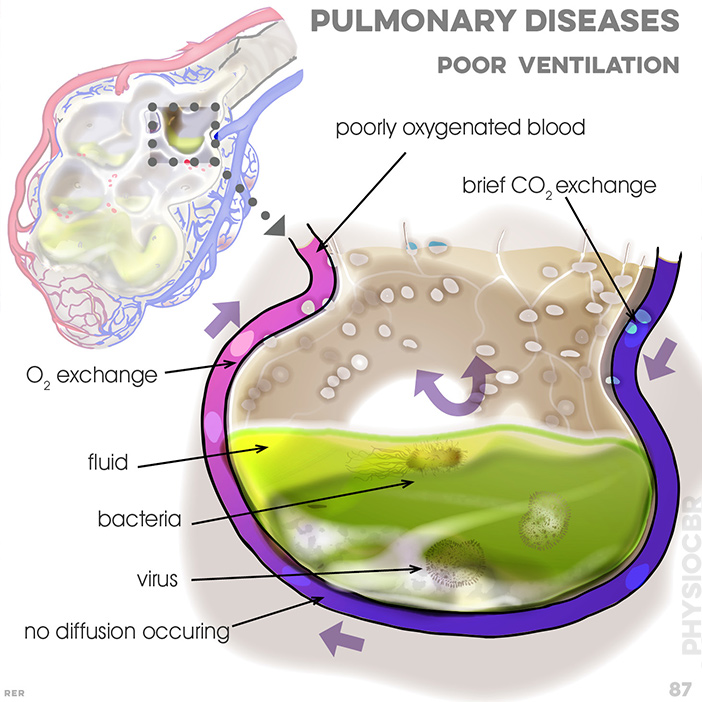
87. Pulmonary disease and poor ventilation: poorly oxygenated blood; brief CO2 exchange; O2 exchange; fluid; bacteria;
virus; no diffusion occuring
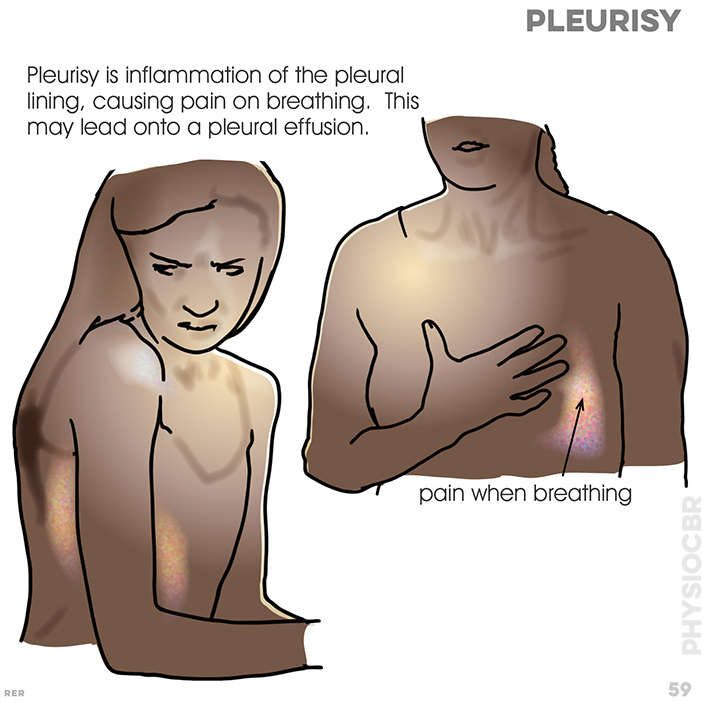
59. Pleurisy is inflammation of the pleural lining, causing pain. This may lead onto a pleural effusion
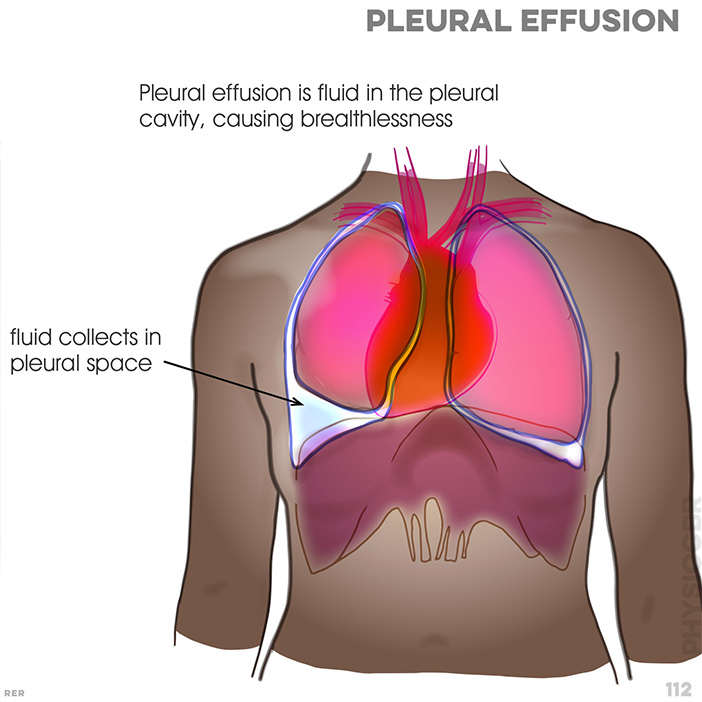
112. Pleural effusion is fluid in the pleural cavity, causing brealthlessness. (not sure yet what needs to differentiate from previous image!)
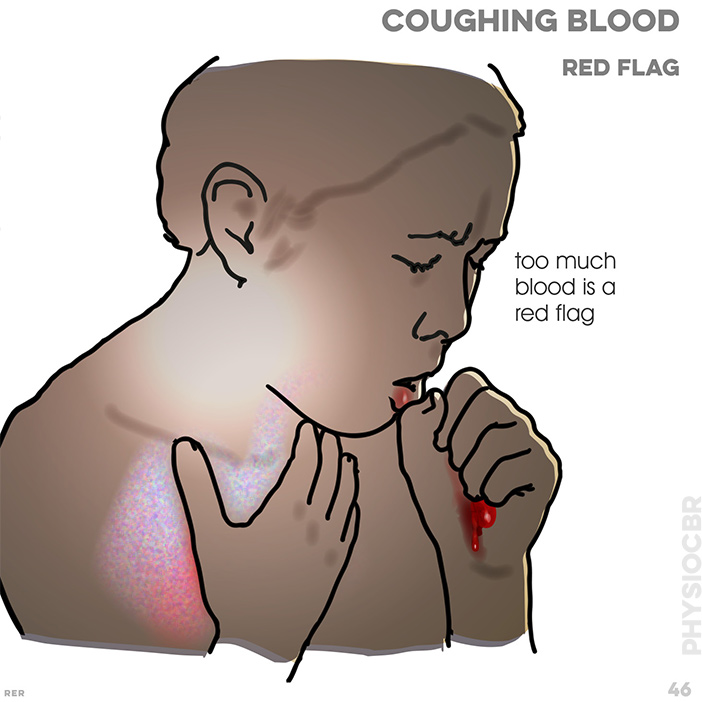
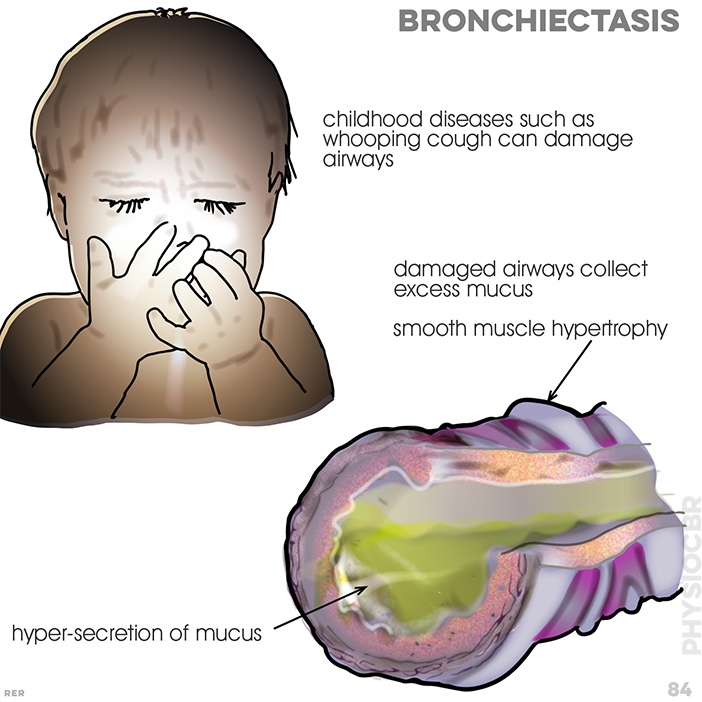
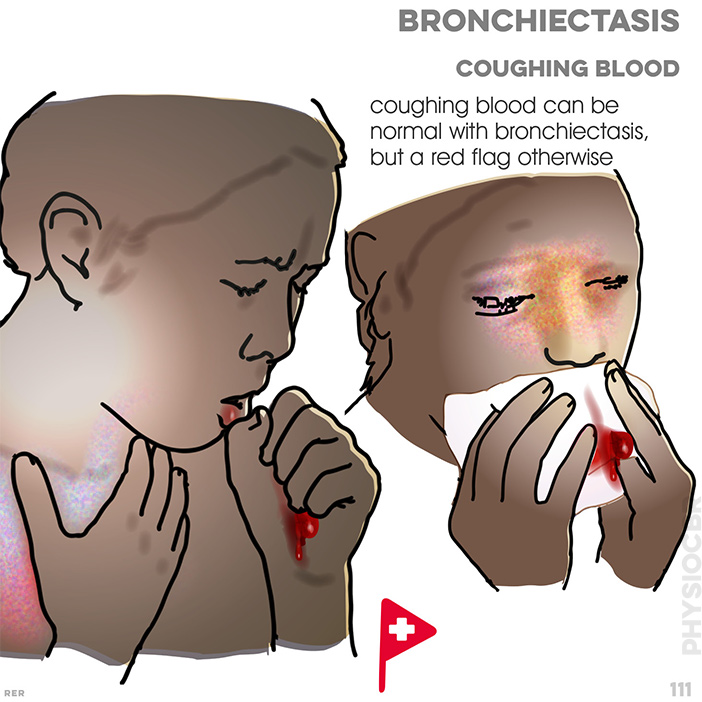
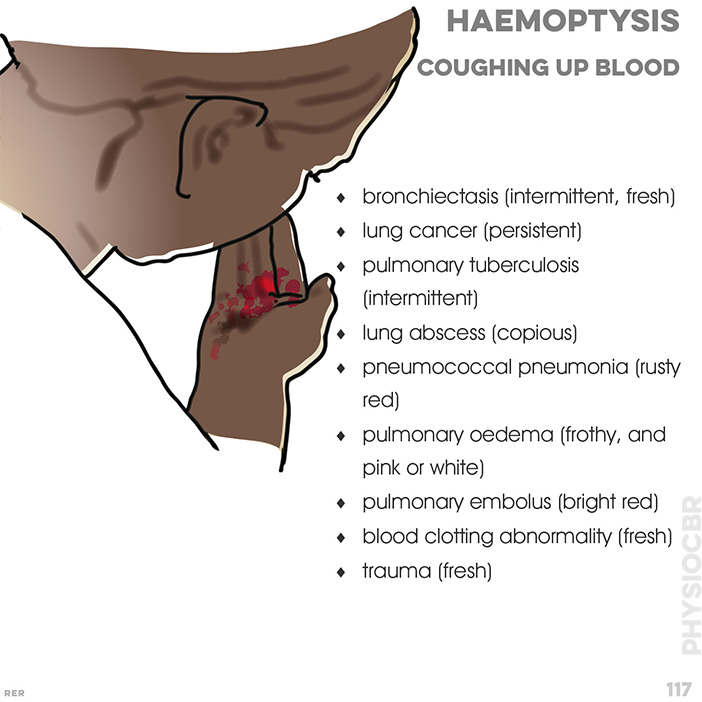
- • bronchiectasis (intermittent, fresh)
- • lung cancer (persistent)
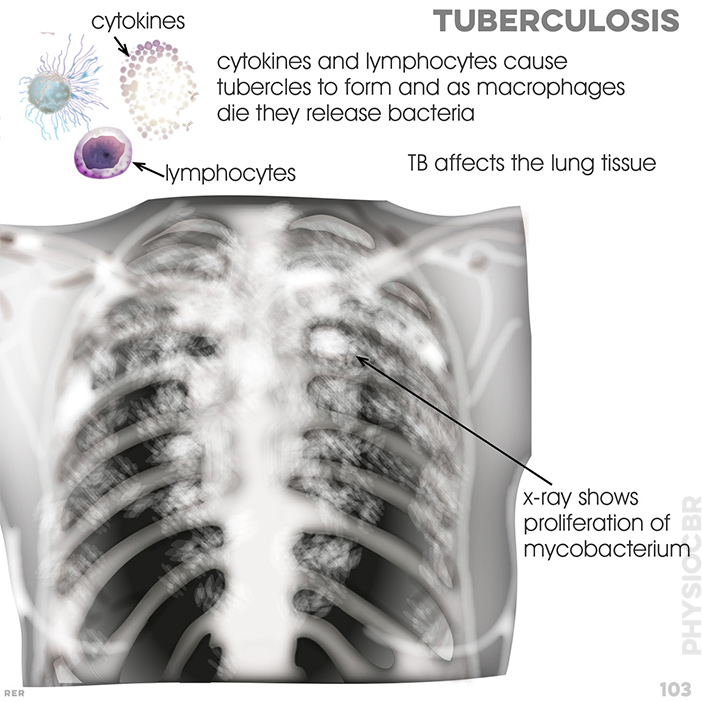
- • pulmonary tuberculosis (intermittent)
- • lung abscess (copious)
- • pneumococcal pneumonia (rusty red)
- • pulmonary oedema (frothy, and pink or white)
- • pulmonary embolus (bright red)
- • blood clotting abnormality (fresh)
- • trauma (fresh)
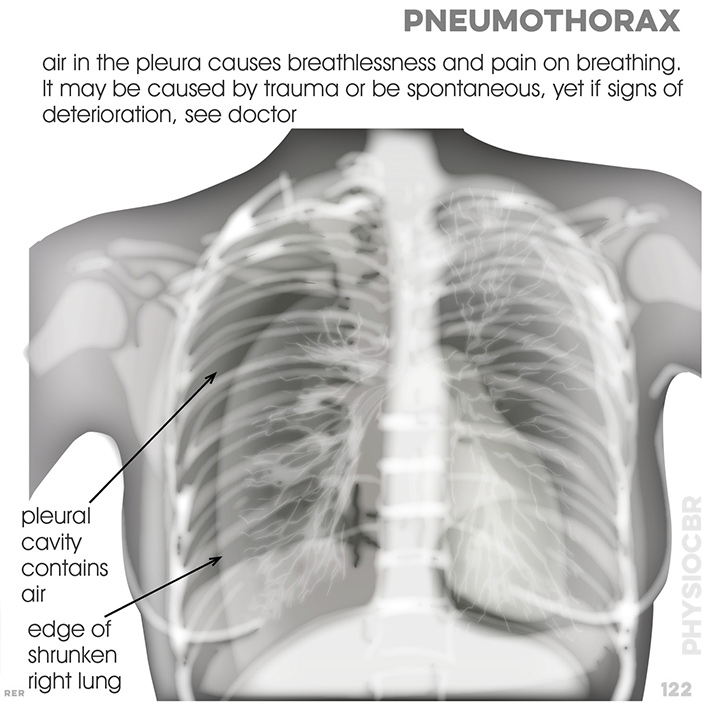
122. Pneumothorax: air in the pleura causes breathlessness and pain on breathing. it may be caused by trauma or be spontaneous, yet if
signs of deterioration, see doctor; air in pleural cavity; edge of shrunken right lung
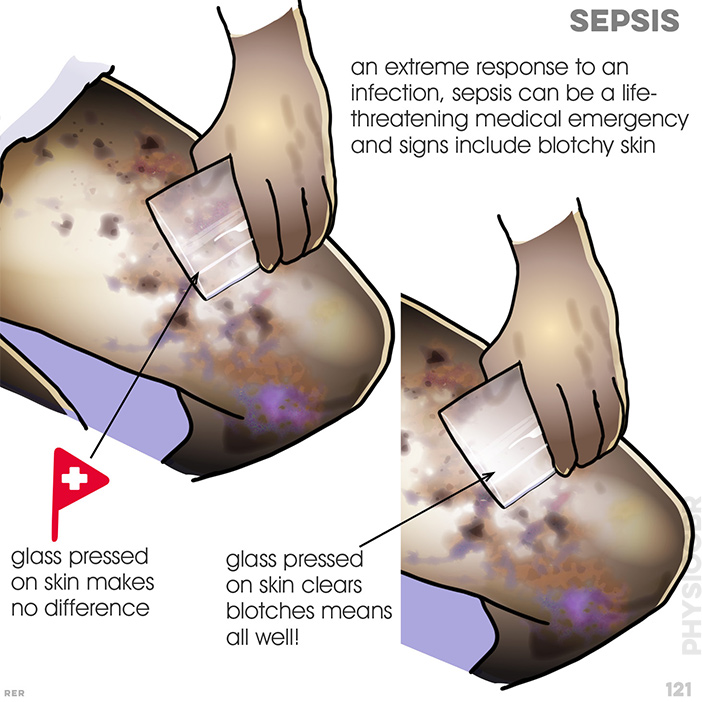
121. Sepsis: an extreme response to an infection, sepsis can be a life-threatening
medical emergency and signs include blotchy skin; glass pressed on skin makes no difference is a warning; glass pressed on skin clears blotches means all is well
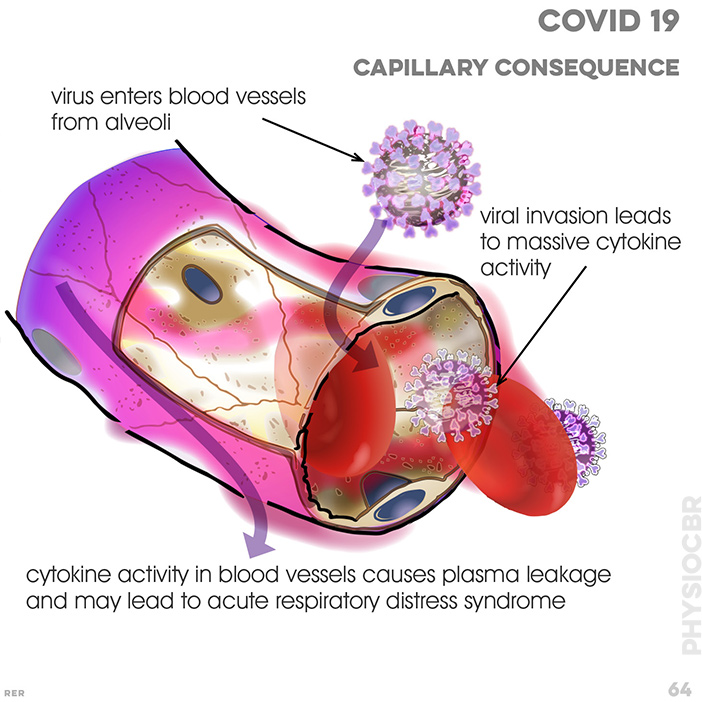
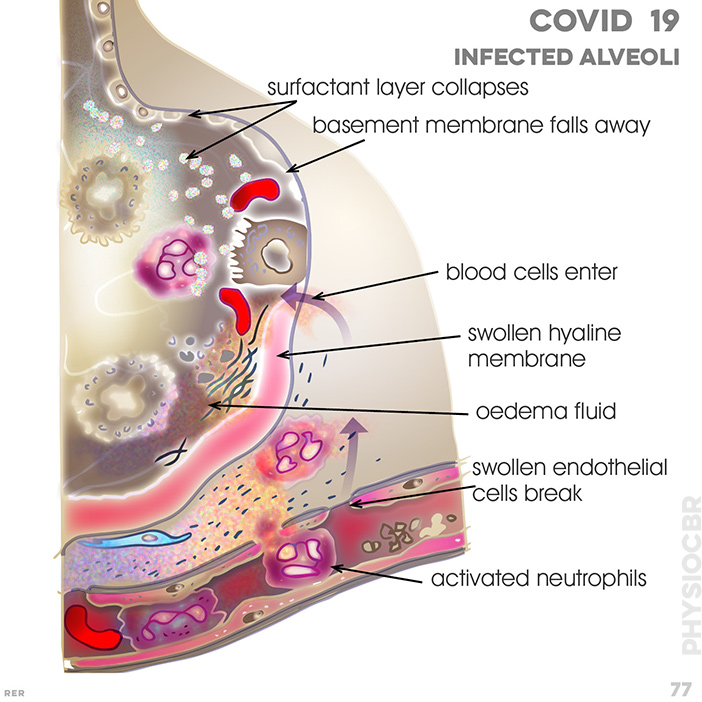
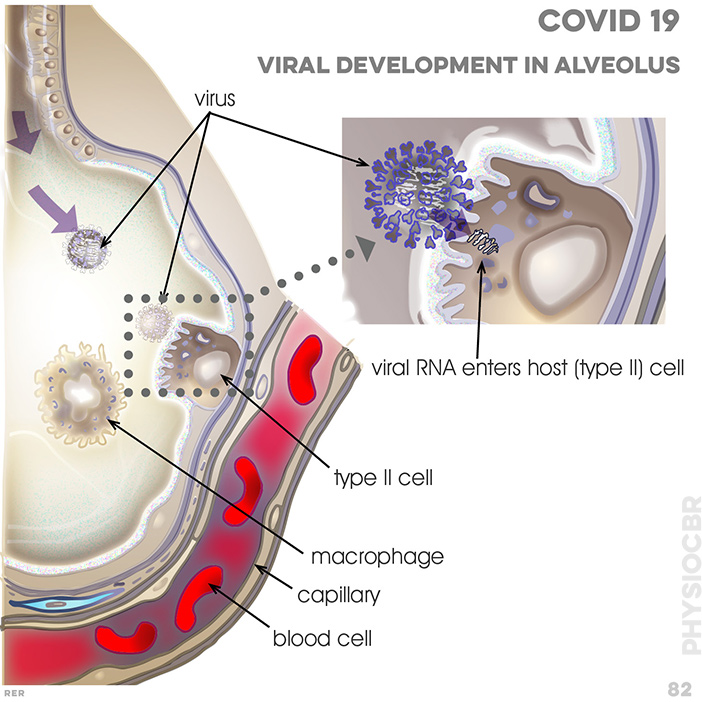
82. COVID19 and viral development in alveolus: viral RNA enters host (type II cell); type II cell; macrophage; capillary; blood cell
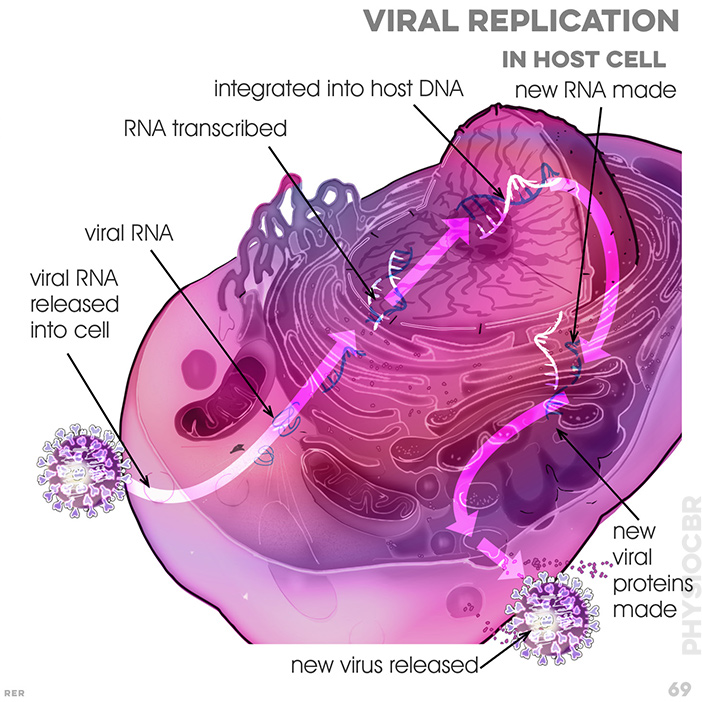
69. Viral replication in host cell: viral RNA released into host cell; RNA transcribed; integrated into host DNA; new RNA made; new viral proteins made; new virus released
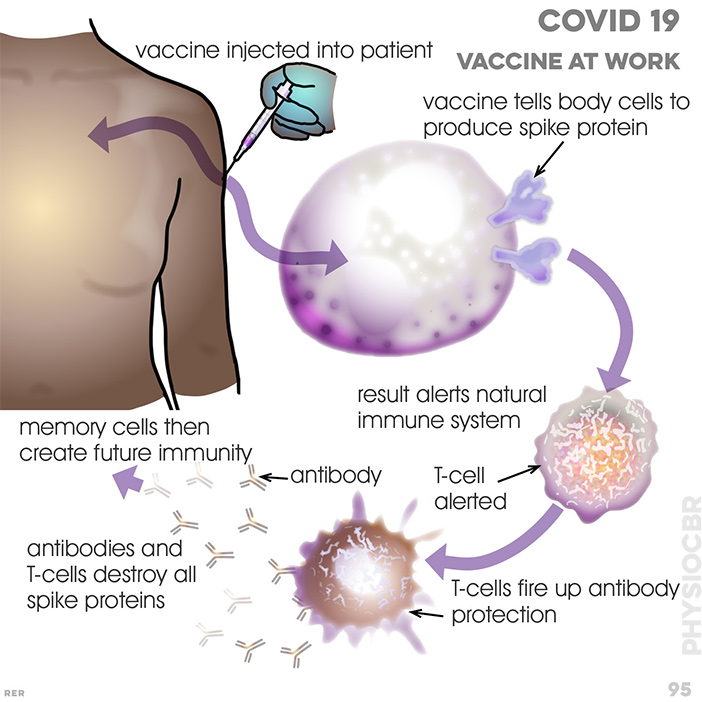
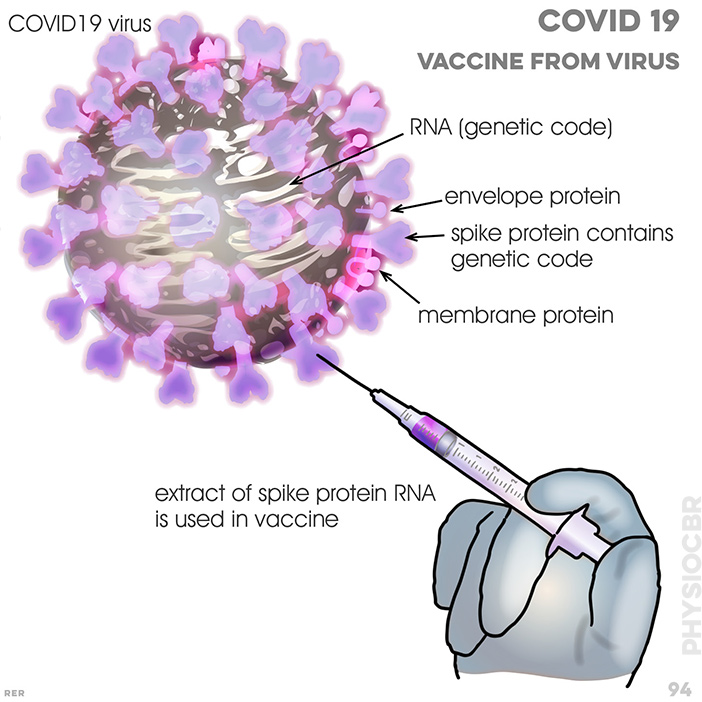
94 COVID 19 and vaccine made from virus. RNA (genetic code); envelope protein; spike protein contains genetic code; membrane protein; extract of spike protein RNA is used in vaccine
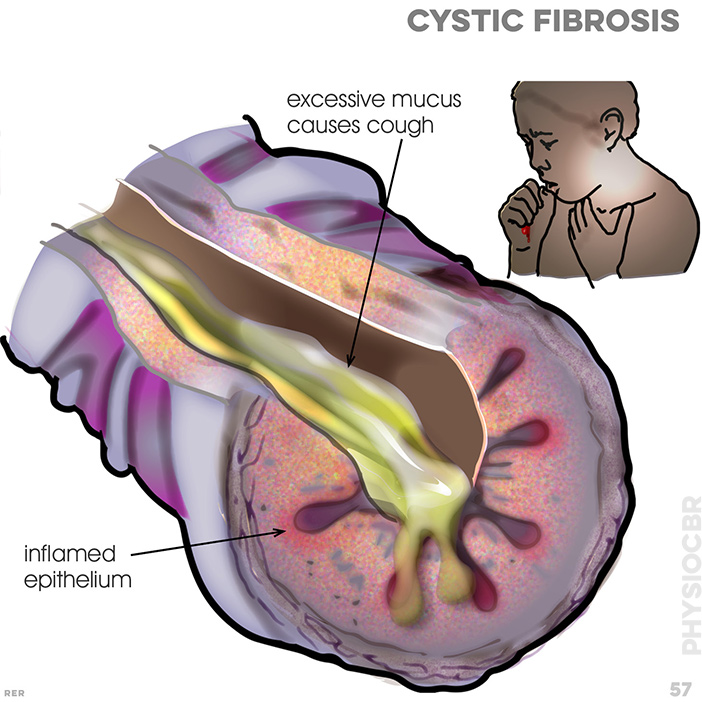
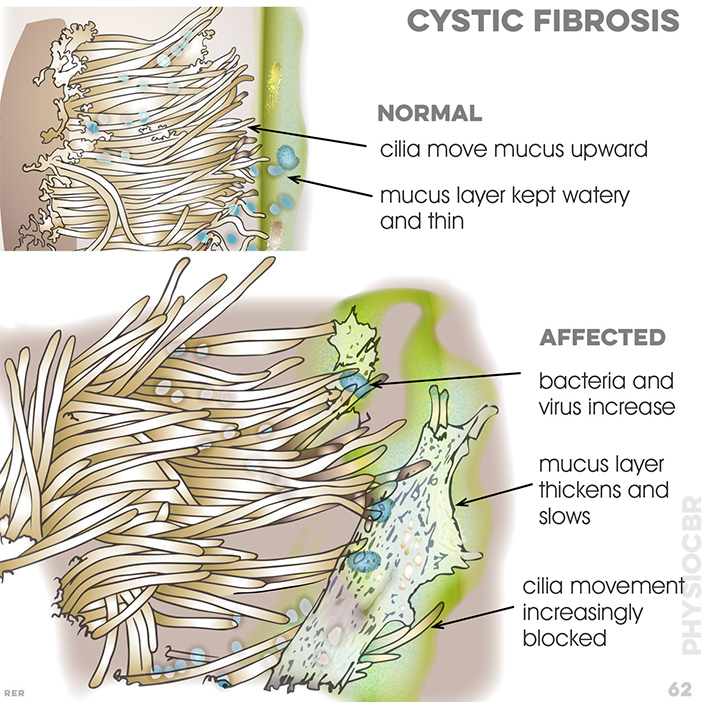
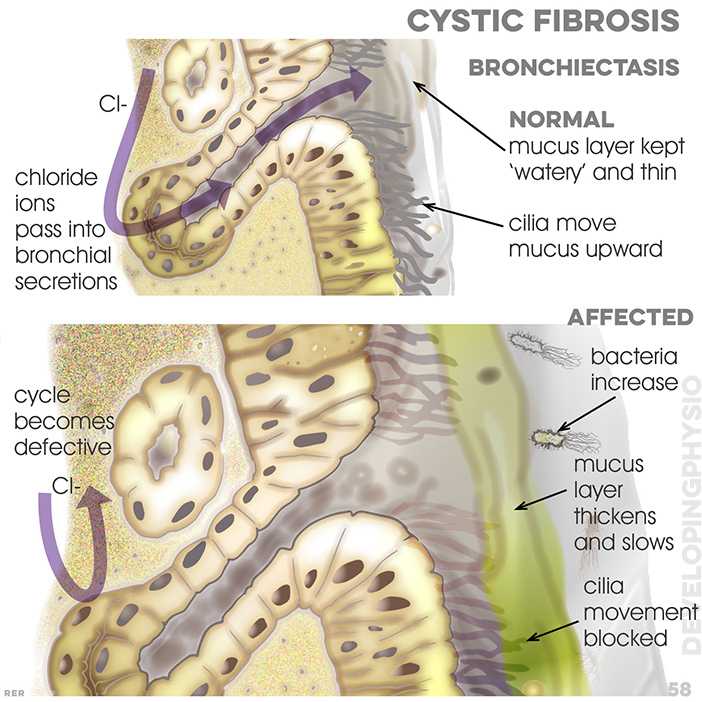
58 Cystic fibrosis, bronchiectasis. normal conditio where mucus is kept 'watery' and thin and cilia move mucus upward. cholride ions pass into bronchial secretions. Affect condition: bacteria increase. mucus layer thickens and slows and cilia movement becomes blocked. ion cycle becomes defective
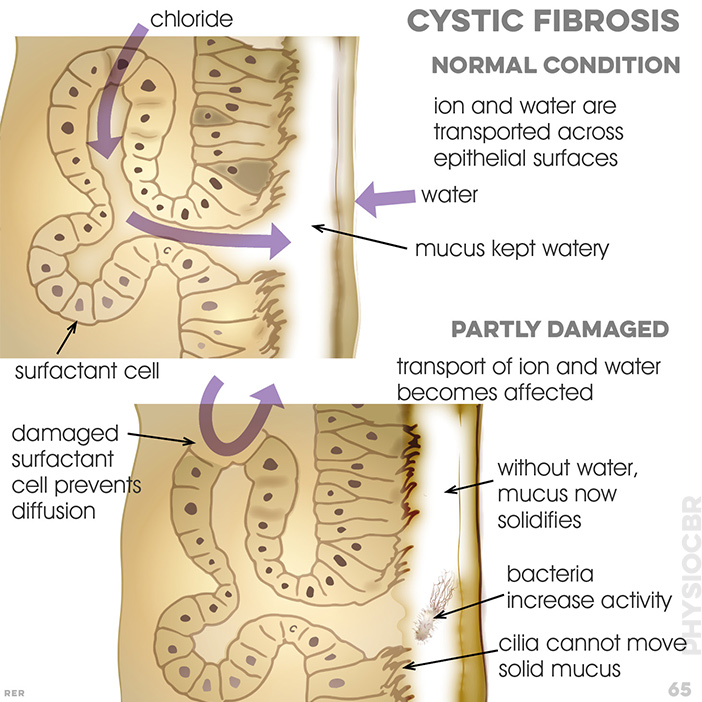
65 Cystic fibrosis, normal condition. ion and water are transported across epithelial surfaces and mucus kept watery. partly damaged conditin: transport becomes affected as, without water, mucus now solidifies, bacteria increase activity and cilia cannot move solid mucus. damaged surfactant cells prevents diffusion
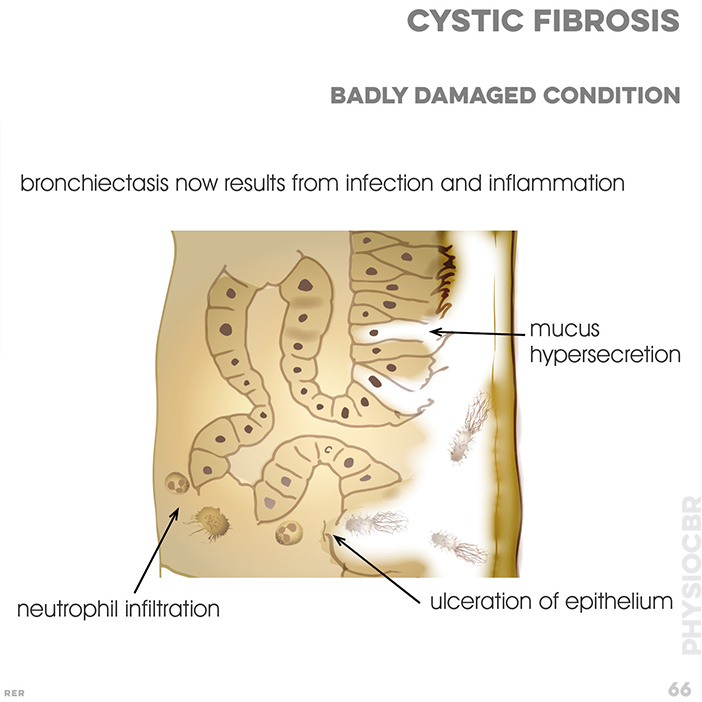
66. Cystic fibrosis, badly damaged condition. bronchiectasis now results frm infection and inflammation. mucus hypersecretion; neutrophil infiltration; ulceration of epithelium
Further material useful?
If you have any thoughts on anything that might help you or your students, please complete this quick feedback memo, which should only take a minute!