Physiology
home | anatomy | physiology | pathology | clinical guides

32. Respiration: measuring breaths per minute, average is 12 - 20 per minute
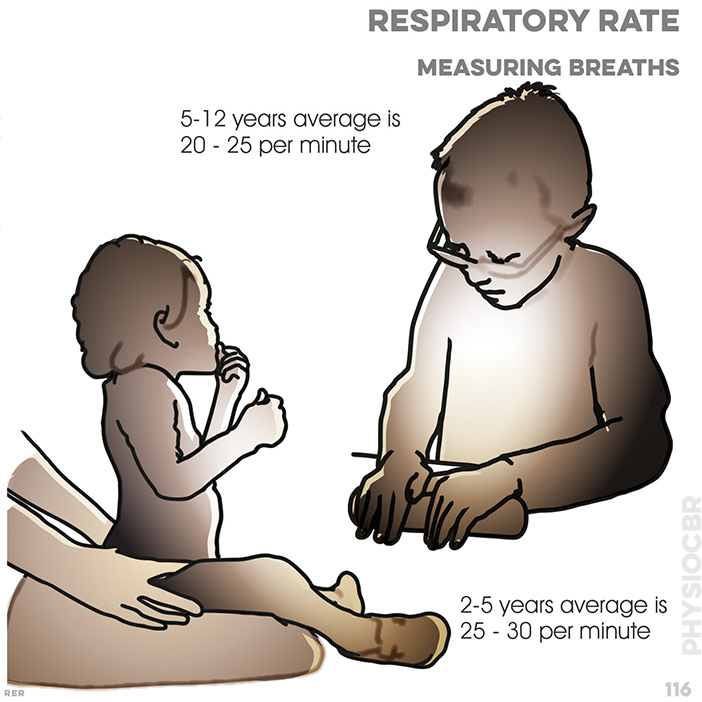
116. Respiration breath rate per minute: 2-5 years average is 25-30; 5-12 years average is 20-25 per minute
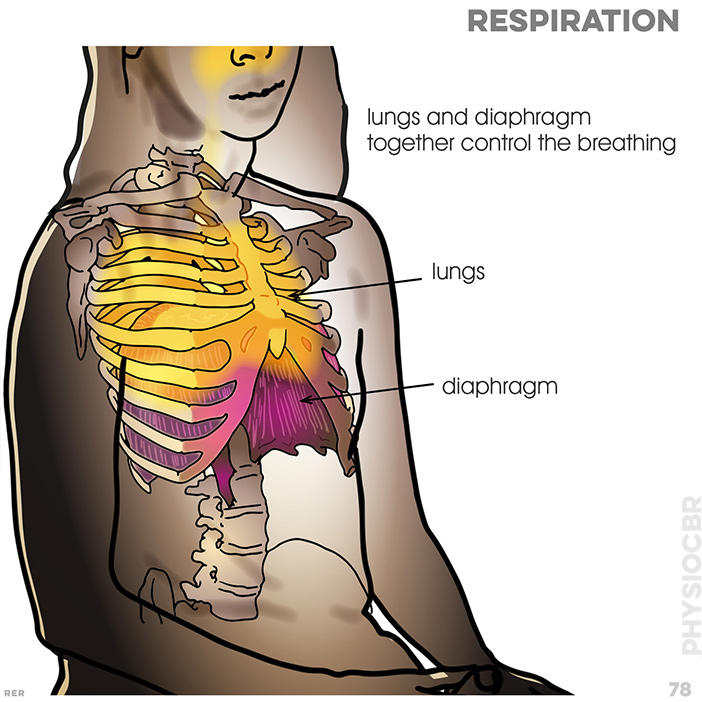
78. lungs and diaphragm together control the breathing
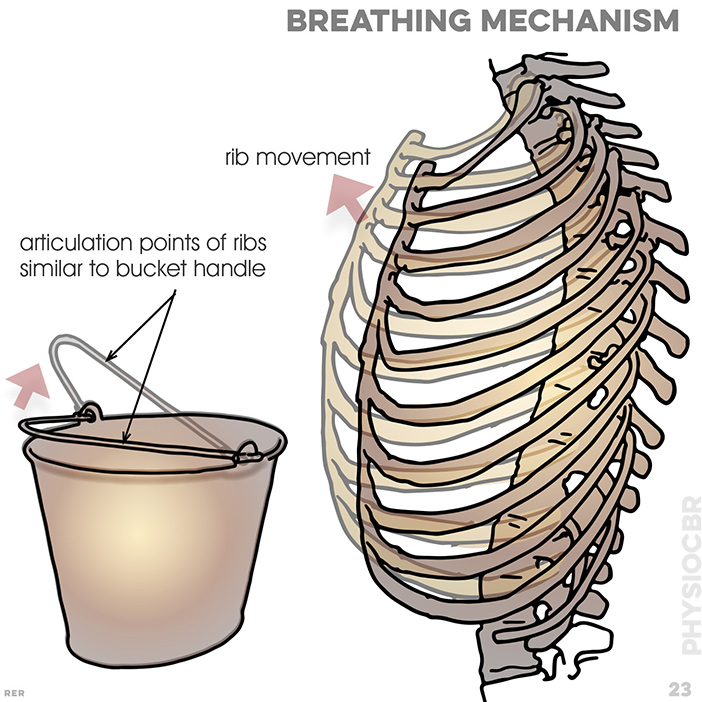
23. Breathing mechanism: ribs articulate to vertebrae; articulation points of ribs are similar to a bucket handle
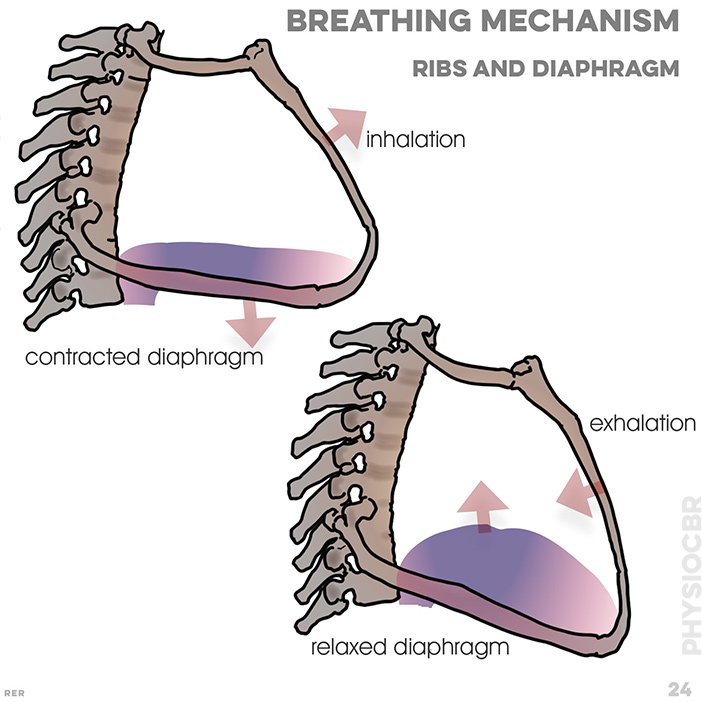
24. breathing mechanism: inhalation, contracted diaphragm; exhalation, relaxed diaphragm; water pumps acts (contracts) like a diaphragm
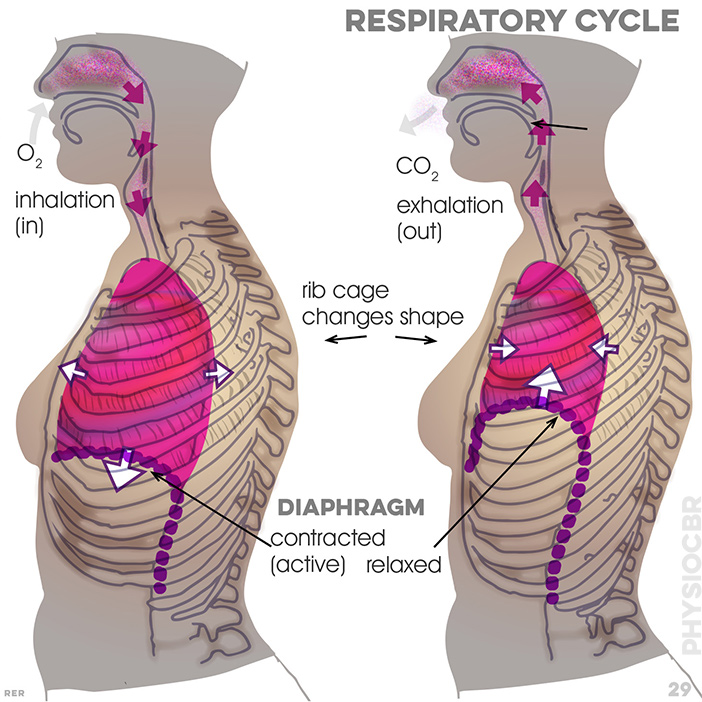
29. Respiration: exhalation; CO2, diaphragm relaxed; inhalation; oxygen breathed in; diaphragm contracted (active)
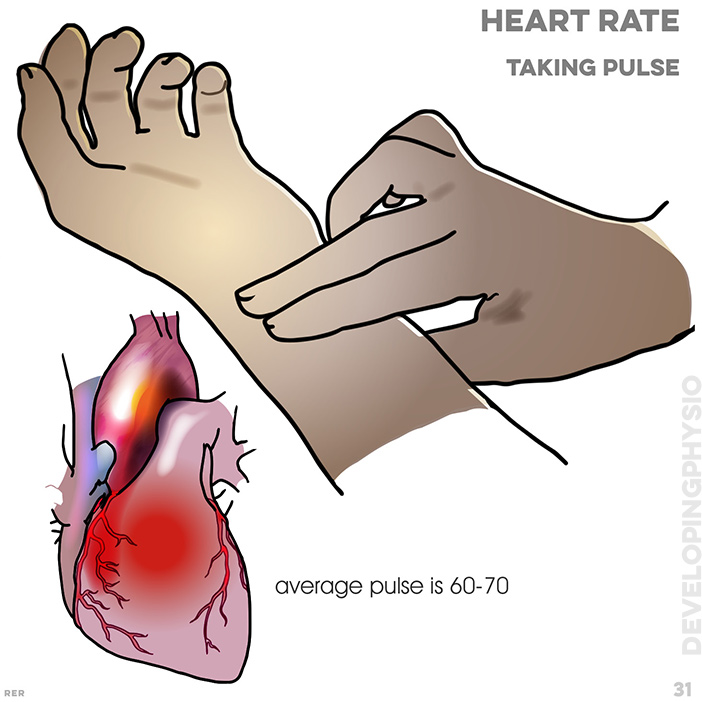
31. Heart rate: taking pulse from wrist, average is 60-70
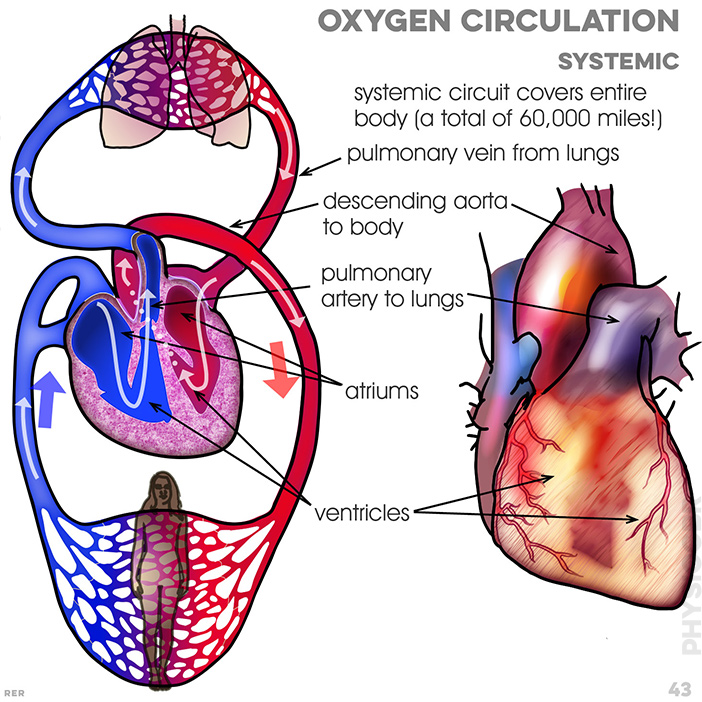
43. Circulation: Systemic circuit covers the entire body
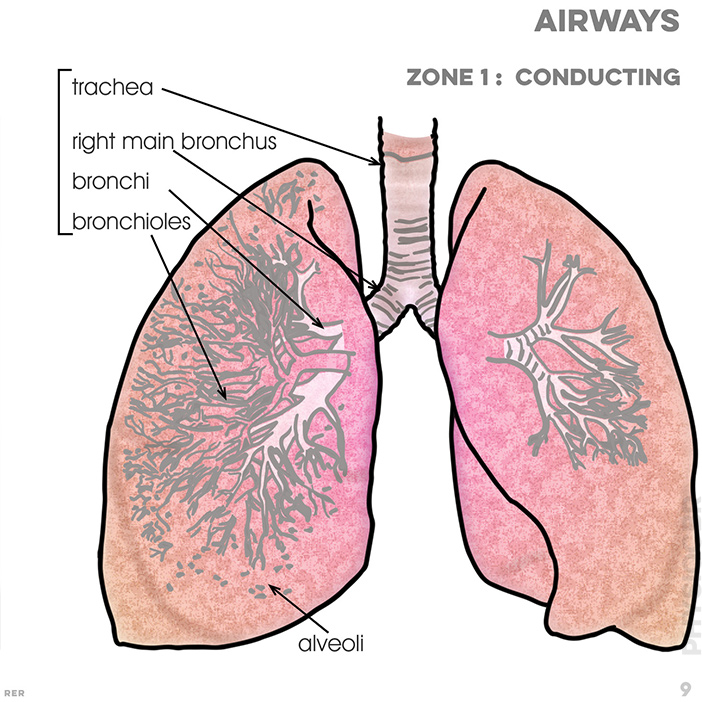
9. Airways: left bronchus; bronchi; bronchioles; bronchioles branch into network so alveoli

10. Alveoli, air transfer: pulmonary from heart; pulmonary to heart; bronchiole; bronchiolar muscle; alveoli
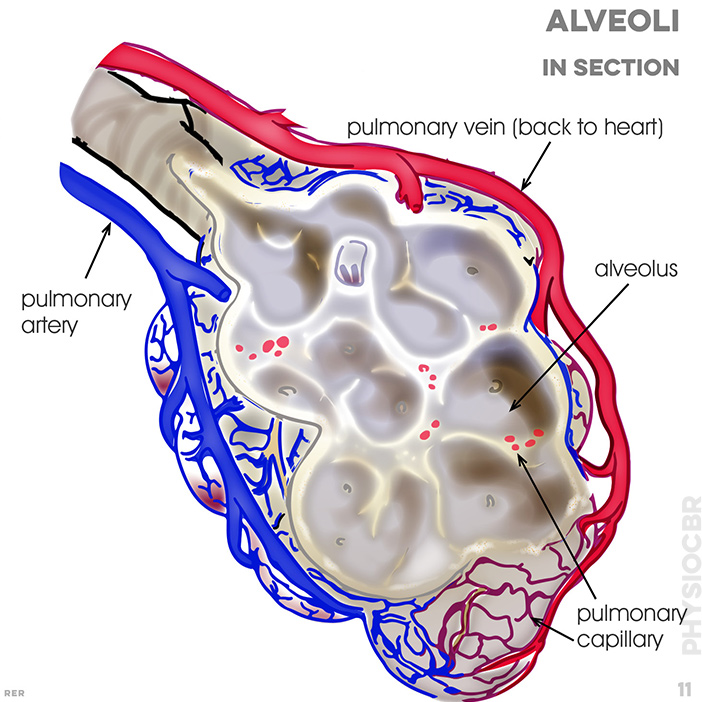
11. Alveoli in section: pulmonary vein; alveolar sac; pulmonary capillary; pulmonary artery
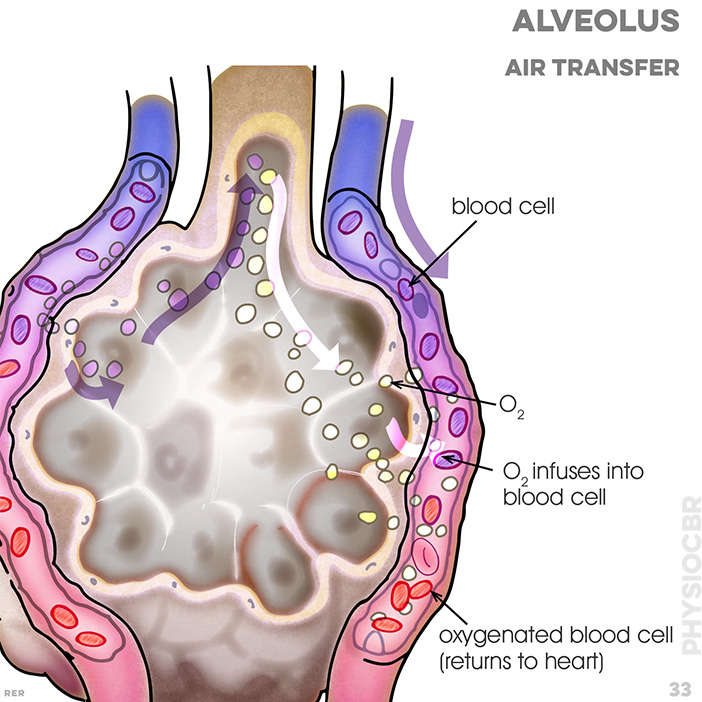
33. Alveoli: capillary wall; red blood cell (from heart); direction of blood flow; oxygentated blood cell (returns to heart)
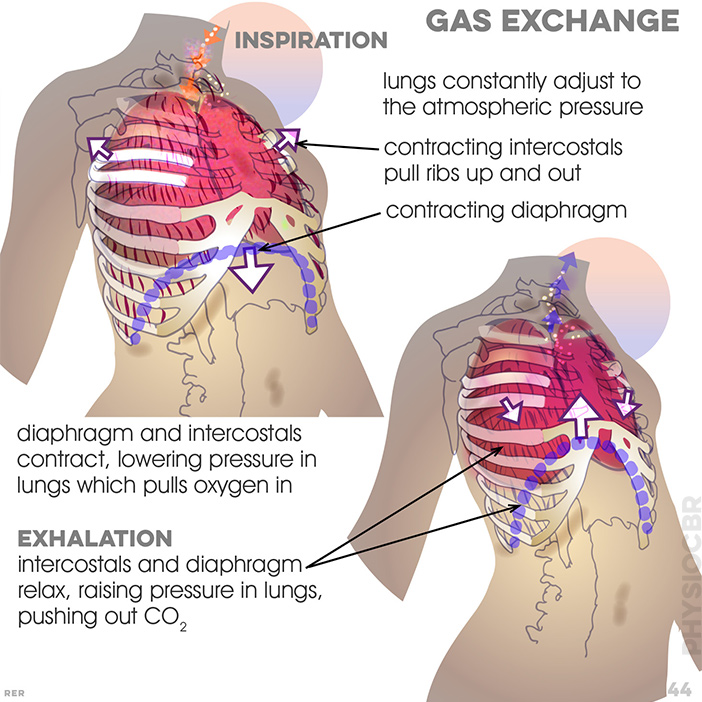
44. Gas exchange. lungs constanty adjust to atmosphere; 1: diaphragm and intercostals contract, lowering pressure pulling in oxygen and then 2: relax, raising pressure, pushing out the CO2
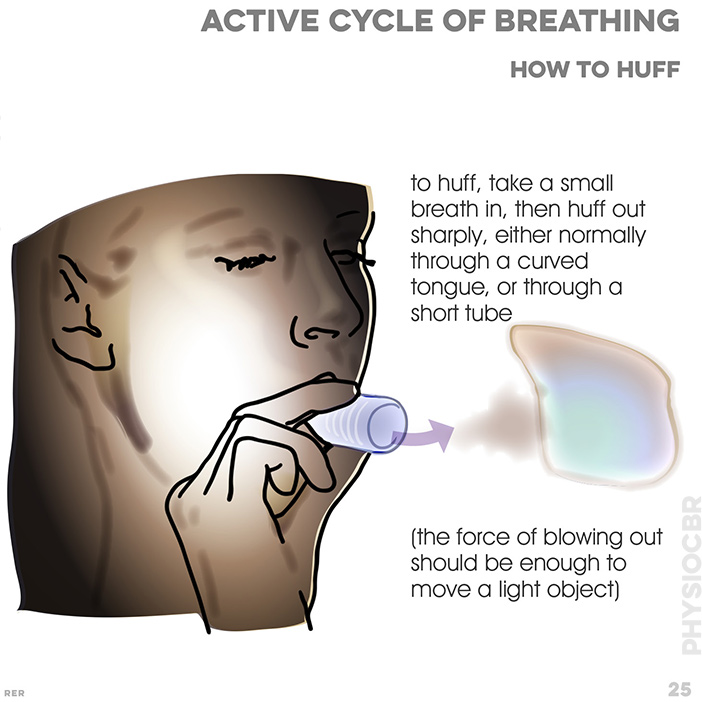
25. Active cycle of breathing techniques (ACBT). To huff, take small breah in and huff out sharply, either through curved tongue or short tube (enough to move a light object)
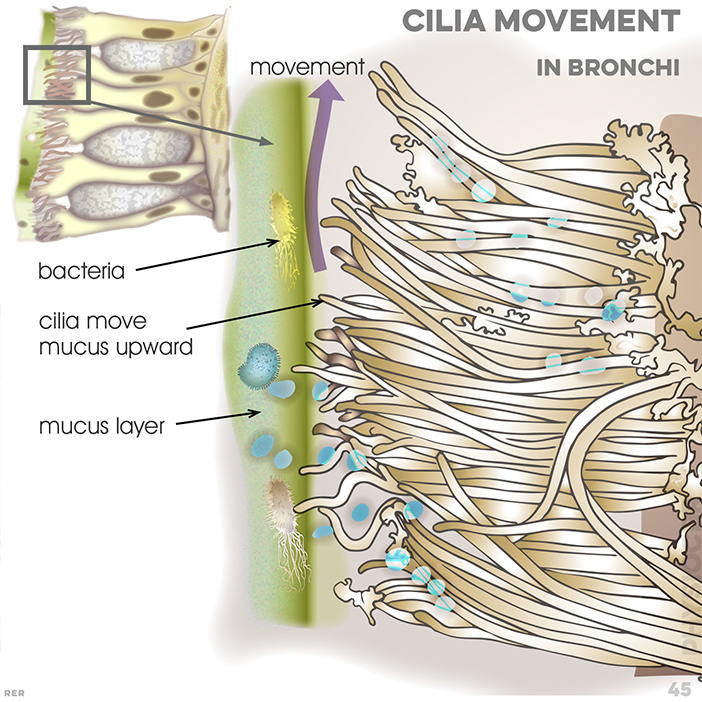
45. Bronchi and cilia movement: bacteria; cilia move mucus upwards; mucus layer kept watery and thin
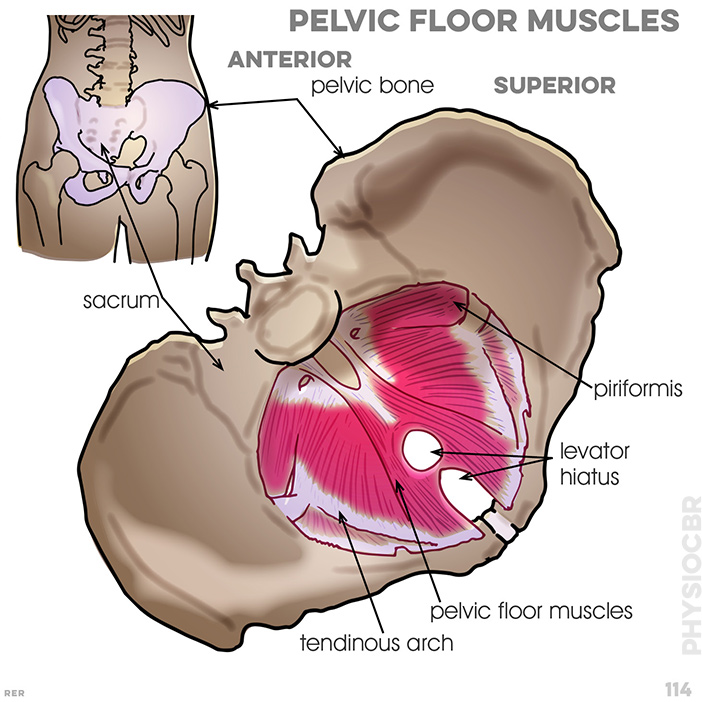
114. Pelvic floor muscles: pelvic bone, sacrum; piriformis, levator hiatus, pelvic floor muscles, tendinous arch

![]() Quick quiz? on physiology
Quick quiz? on physiology
arrow_rightImmediate thoughts for students?
![]() Feedback memo while you remember it!
Feedback memo while you remember it!
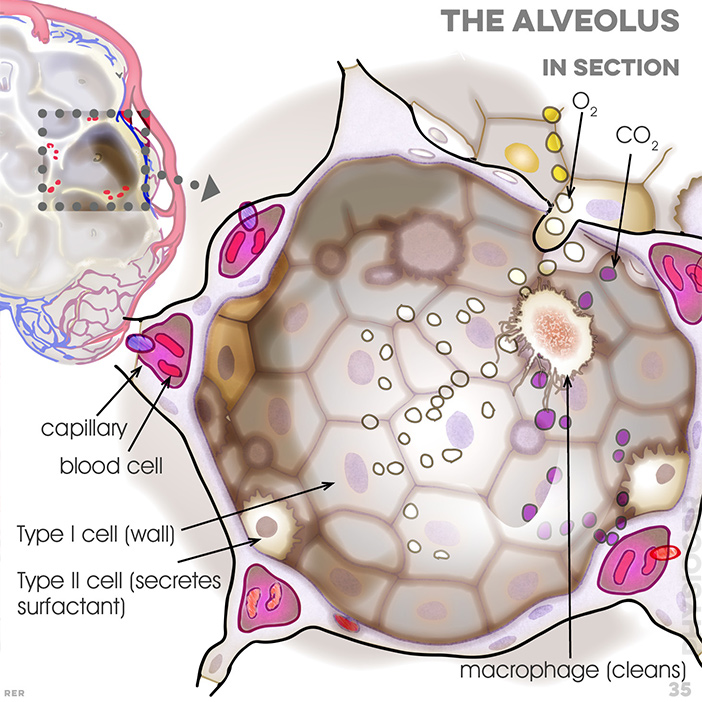
35. Inside the alveolus, maintaining balance:
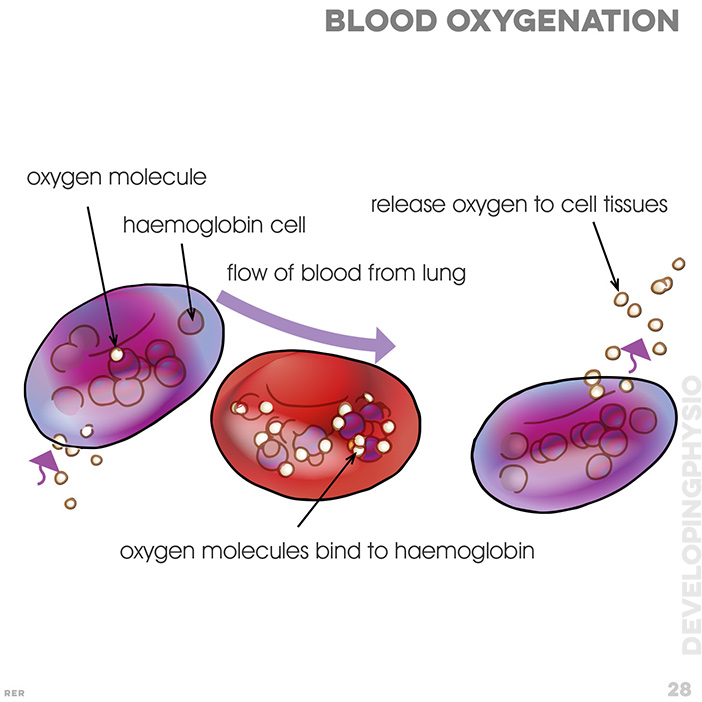
28. Blood oxygenation: oxygen molecule; haemoglobin cell; flow of blood from lung; release oxygen to cell tissue; oxygen molecules bind to haemoglobin

40. Gas exchange. carbon dioxide; exhaling alveoli (deflated); low concentration; membrane; high concentration of CO2
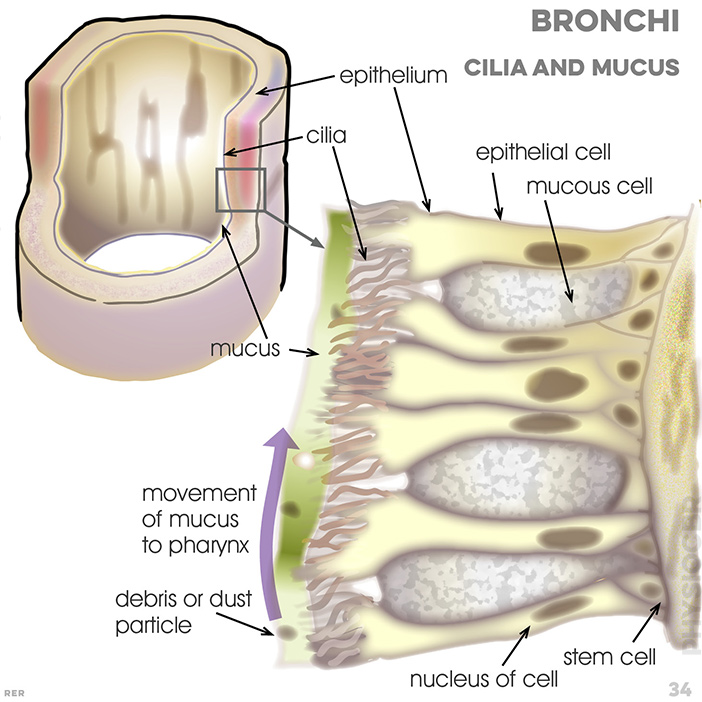
34. Respiration, epithelium: cilia; mucus; epithelial cell; mucous cell; movement of mucus to pharynx; debris or dust particle; nucleus of cell; stem cell
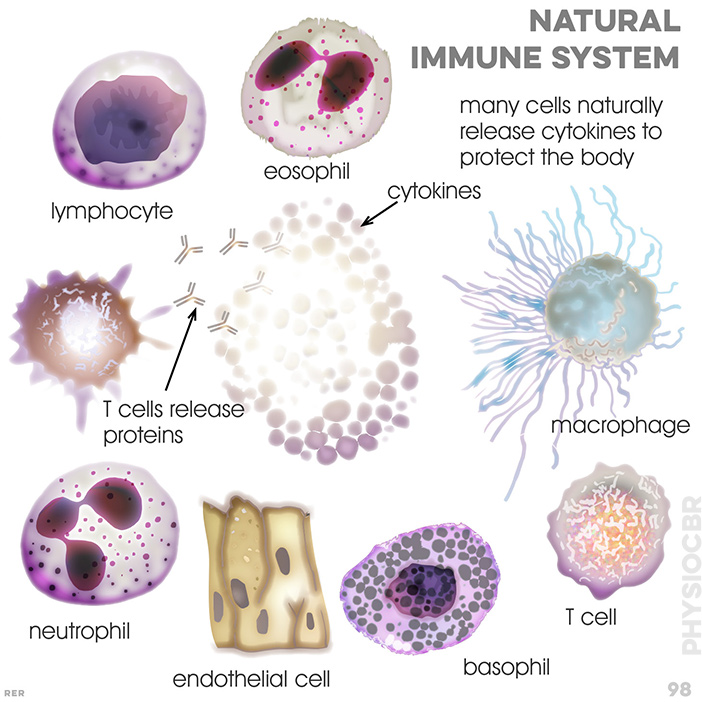
98. natural immune system: many cells release cytokines to protect the body; macrophage, T cell; basophil, endothelial cell, neutrophil, lymphocyte, eosophilitochondrion
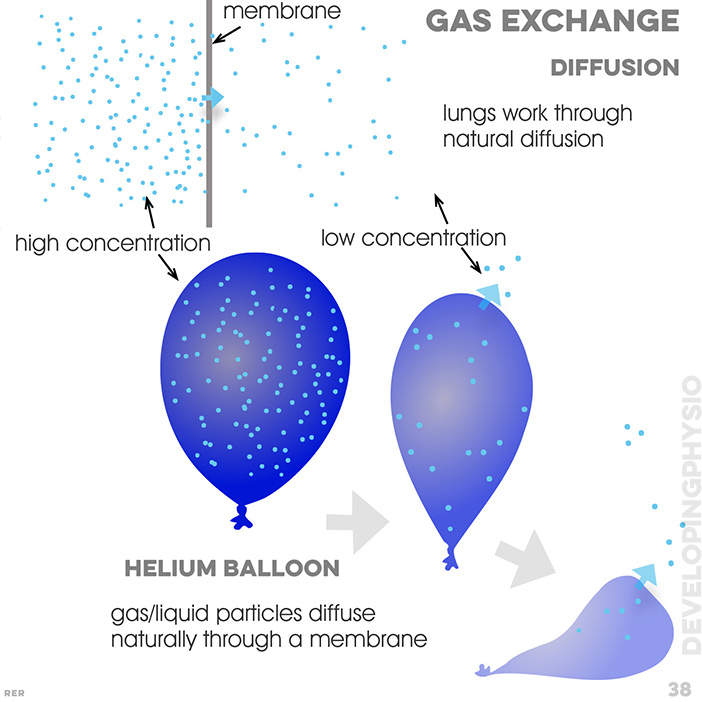
38. Gas exchange. diffusion: lungs work through natural diffusion; membrane; high concentration; low concentration; helium balloon: gas/liquid particles diffuse naturally through a membrane
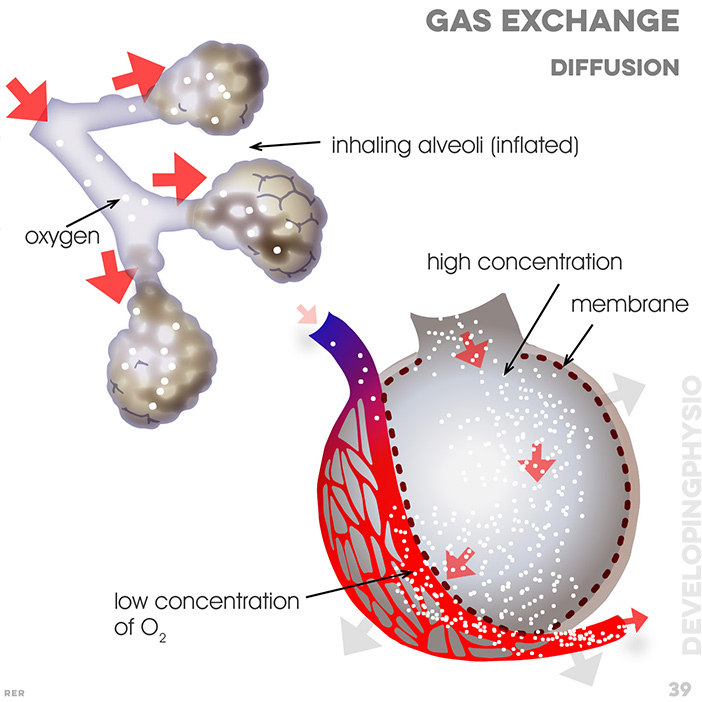
39. Gas exchange. inhaling alveoli (inflated); oxygen; high concentration; membrane; low concentration of O2
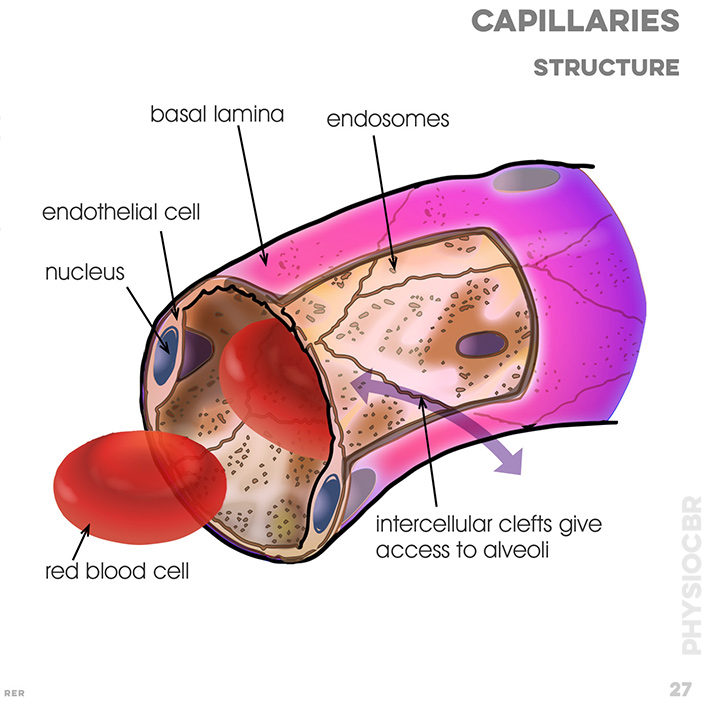
27. Capillaries, structure: basal lamina; endothelial cell; nucleus; pores (fenestrations); endosomes
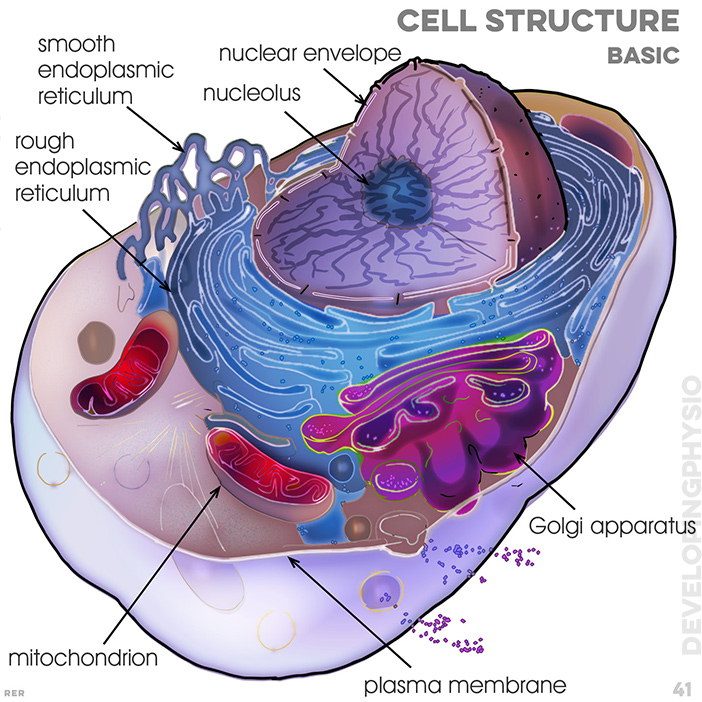
41. cell structure (basic): rough endoplasmic reticulum; smooth endoplasmic reticulum; nucleolus; nuclear envelope; golgi apparatus; plasma membrane; mitochondrion
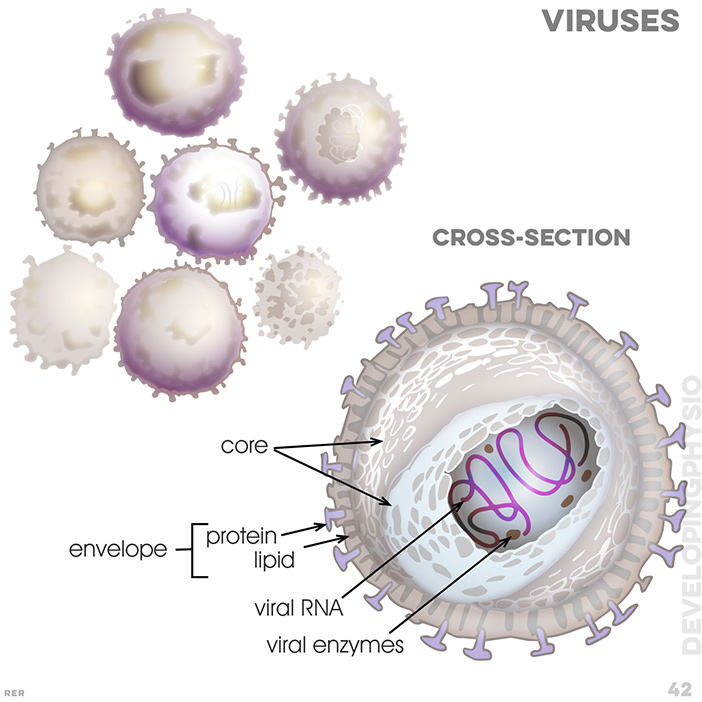
42. viruses: core, envelope containd protein and lipid; viral RNA; viral enzymes
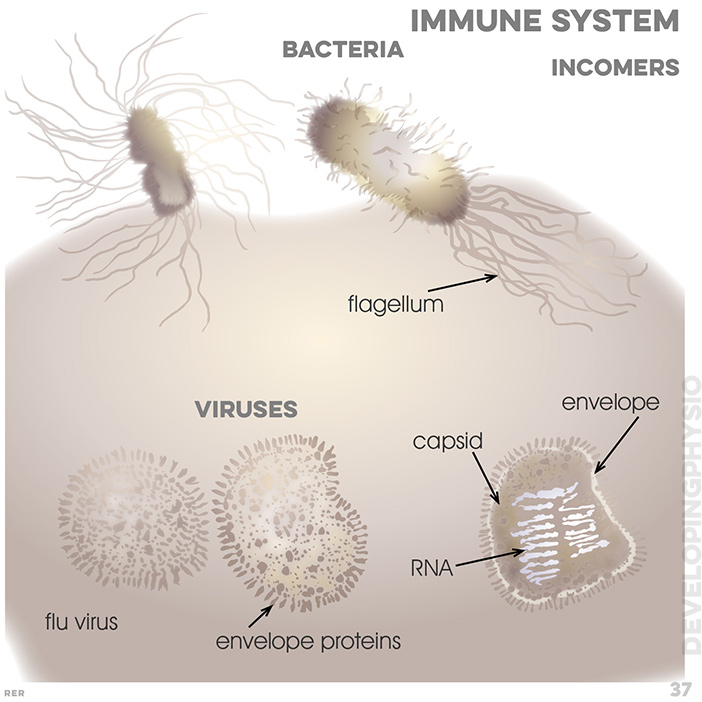
37. Immune system, incomers: bacteria, flagellum; viuses: flu virus; envelope proteins; RNA; capsid; envelope

![]() Quick quiz? on physiology
Quick quiz? on physiology
arrow_rightImmediate thoughts for students?
![]() Feedback memo while you remember it!
Feedback memo while you remember it!
The active cycle of breathing technique (ACBT) is a three-stage process for clearing sputum whilst Breathing dynamics shows how rib movement creates the conditions for breathing and breathing and gas transfer introduces the alveoli
The first stage: The process is gentle and rhythmic and a hand on the chest may help. (note that the lungs, at the point of full in-breath, diffuse the gas exchange of oxygen from alveoli into the blood vessels and, similarly, carbon dioxide diffuses back into the alveoli when gas pressure is lowest and the lungs are contracting).
Also called 'thoracic expansion': Deep breathing involves holding the breath for a second or two (if possible) to encourage diffusion (or transfer of oxygen within the alveoli). After deep breathing, a few more relaxed breaths are recommended before continuing to the third 'huff' stage.
The critical stage: The huff is the point when the sputum is released, however if release is only partially successful, simply relax and repeat the three steps.. it is a process and not a test!